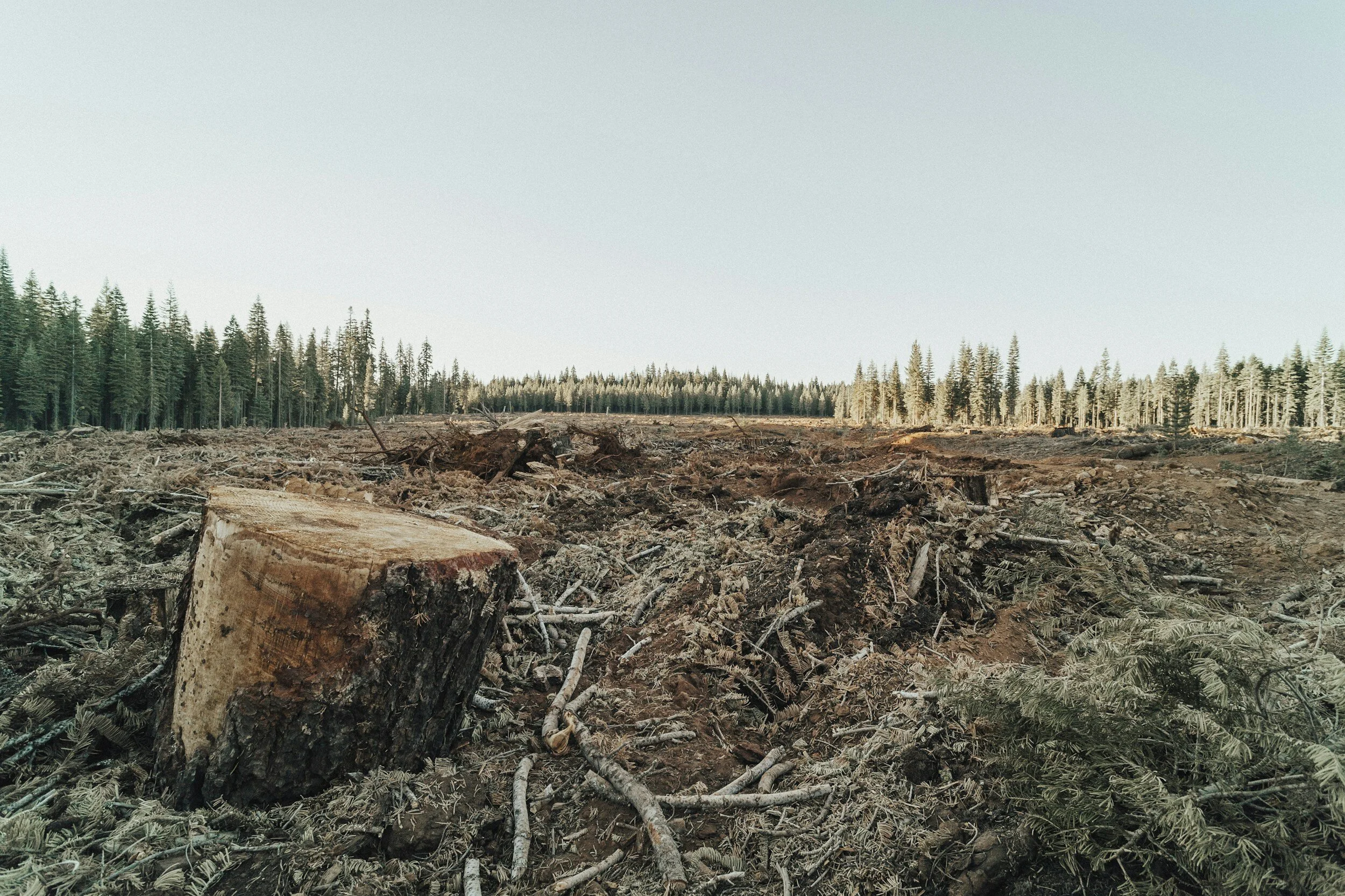
EU's Deforestation Crackdown is Underway
Deforestation is a major global problem, with agriculture responsible for a whopping 90% of it. The scale is staggering - we're losing an area the size of a football field every two seconds.
The demand for goods like cocoa and coffee is a big driver of deforestation, and the EU is a key player in this. Michael Rice from ClientEarth points out that the EU ranks second only to China in importing deforestation-linked products.
To tackle this, the European Commission is rolling out new rules to crack down on products tied to deforestation. Starting December 2024, anyone trading with the EU has to prove their goods aren't coming from recently deforested areas.
It's a move aimed at fighting climate change and protecting biodiversity, but it comes with teeth - hefty fines, product confiscation, and even bans for those who don't play by the rules. While many see it as a step towards sustainability, others worry about its effectiveness and impact on trade.
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
Starting in December 2024, the EU's got new guidelines that demand solid proof goods aren't linked to deforestation, and they're not messing around - fines and even bans are on the table for those who don't follow the rules. This shift means it's time for industry folks to rethink how they handle their supply chains, making sure they're on the right side of the law and avoiding any hefty penalties.
Plus, it's nudging companies to think greener when it comes to sourcing and moving stuff around, all in line with helping out the planet and keeping trade running smoothly.
🔥 OUR HOT TAKE?
The EU's crackdown on deforestation-linked products is a bold move with global implications. While it's a step in the right direction for fighting climate change and preserving biodiversity, the potential impact on trade dynamics is a cause for concern. With hefty fines and bans in the picture, businesses trading with the EU face increased pressure to clean up their supply chains. This could spark a broader shift towards sustainable practices in the industry, but it also raises questions about the feasibility and fairness of enforcement. Overall, it's a complex issue that highlights the delicate balance between environmental protection and economic interests on the global stage.
A top cybersecurity firm, ESET, has uncovered Chinese hacking attempts in the European cargo shipping industry, marking the latest instance of China-aligned groups infiltrating Western economic infrastructure.
In the Netherlands, a new European Hyperloop Center has just opened, featuring a quarter-mile long white steel tube that might revolutionize how we travel and transport goods.
Deforestation is a major global problem, with agriculture responsible for a whopping 90% of it.
The development of a European battery supply chain for electric vehicles independent of China is facing significant delays as companies shift their focus to the US market due to clean energy subsidies offered by the US Inflation Reduction Act.
France, Germany, and Italy have opposed the EU's draft AI legislation, particularly regulations concerning "foundation models" that underpin large AI language models.
Iceland has declared a state of emergency in response to a series of earthquakes on the Reykjanes peninsula, raising concerns about a potential volcanic eruption.
Orcas have been involved in a series of "attacks" on boats in the waters between southern Europe and northern Africa since 2020, with around 500 encounters reported.
Storm Ciarán swept through Western Europe, bringing record-breaking winds and causing widespread power outages, transportation disruptions, and significant damage.
Germany has allowed France to use state subsidies for its nuclear power plants, breaking a deadlock in EU electricity market reform discussions.
Belgium is investigating potential security risks related to China's Alibaba Group's presence at Liège Airport, where its main European logistics center is located.
The UK government's recent pro-motorist policies have contributed to a "greenlash" against ambitious environmental initiatives in Europe.
Former U.S. President Donald Trump and conservative politicians in Europe are intensifying their criticism of electric cars, making it a campaign issue on both sides of the Atlantic.
New Brexit trade rules related to electric vehicles could impose a significant financial burden on European auto manufacturers, potentially costing them £3.75 billion ($4.58 billion) over the next three years, as reported by BBC News.
Russia continues to depend on European shipping to transport its oil, even as its supplies exceed the price caps set by the Group of Seven (G-7) and its allies, according to the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) based in Helsinki.
Europe is grappling with a severe public health crisis as nearly everyone on the continent resides in areas plagued by dangerous air pollution levels, according to an investigation by The Guardian.
Ships transporting goods in and out of the European Union will soon face significant emissions-related costs as they join the bloc's Emissions Trading System (ETS) starting in January 2024.
Germany, known for its economic prowess, is currently facing a stark reversal of fortune.
The U.S. and EU are taking steps to lessen Asia's stronghold on the global semiconductor market. With the shift of semiconductor manufacturing operations to major Asian countries, the U.S. and Europe have faced challenges in maintaining competitiveness.
Moody's has highlighted that the new Deforestation Regulation introduced by the European Union poses a significant risk to European supply chains.
Sennder, the German digital freight forwarder, has announced the renewal of its joint venture with Poste Italiane, Italy's postal operator.
Abu Dhabi-based AD Ports Group has successfully acquired Noatum, a leading provider of integrated logistics services operating in 26 countries worldwide.
Intel is investing $4.6 billion in a new assembly and testing facility in Poland and expanding its investment in a semiconductor fabrication plant in Germany, totaling approximately $33 billion.
Logistics Plus Inc., a logistics service provider based in Erie, Pennsylvania, has acquired Dutch company Jan Krediet in order to expand its presence in Europe.
Republican lawmakers Senator Tim Scott and Representative James Comer have expressed concerns about European Union (EU) environmental, social, and governance (ESG) measures gaining traction in the United States.
Italy has unveiled plans to establish a €1 billion sovereign fund to support strategic companies and enhance domestic production, aiming to strengthen key supply chains.
European governments have traditionally been more aggressive in regulating fuel consumption, but the United States is catching up with strict emissions regulations and fines for automakers that fail to meet EV sales targets.
Under new EU regulations set to come into force in 2024, European transport and logistics firms, including airlines, airports, and shipping lines, will have to bolster their cybersecurity measures.
A new hydrogen production plant aims to solve the problems with refueling and distribution snags.
Ever since the war started between Russia and Ukraine, many European countries have reverted to using coal and other less environmentally friendly practices.






























A recent judicial move in Milan has put a spotlight on some serious ethical issues in the luxury fashion industry.